Structure function relationships of dUTPases
dUTPase, a key enzyme in processes preventing uracyl incorporation in DNA, is present in all prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is a potential target protein against cancer cells, Mycobacteria and Plasmodia. In a cooperation with the Laboratory of Genome Metabolism and Repair of the Institute of Enzymology, RCNS HAS and Biostruct Laboratory of the Budapest University of Technology and Economics we contributed various crystallographic projects by assisting in structure solution model building and refinement.
Effects of various functionally important residues were clarified using the structures of mutant dUTPases. Asp28, a conserved residue of dUPTase was previously thought to participate in coordination of Mg2+ cofactor. The structure Asp28Asn mutant revealed that its role is more complex. The small disruption of the hydrogen binding network in the Asp28Asn form had far reaching conformational effect causing mobilization of the C-terminal segment of the neighbouring subunit of the trimeric enzyme, responsible for stabilizing the phosphate chain of the substrate. We studied the effect of the interaction of the uracyl ring of the substrate and the conserved aromatic residue of dUTPase on the catalytic activity. Structures of H145W and H145A mutant forms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis dUTPase in comparison with the native enzyme together with solution kinetic studies led to the conclusion that this interaction highly contributes to the stabilization of the transition state of the phosphate ester hydrolysis reaction. The structural studies include dUTPase of Mason-Pfizer monkey betaretrovirus, a fusion protein containing the nucleocapsid domain as well.
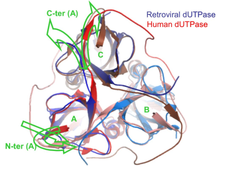
Comparison of the structures of human and retroviral dUTPases
Cooperation:
Laboratory of Genome Metabolism and Repair of the Institute of Enzymology, RCNS of the Hungarian Academy Sciences, Budapest
Biostruct Laboratory of the Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Budapest
Related publications
-
Veronika Németh-Pongrácz , Emese Kónya , Katalin F. Medzihradszky , Éva Hunyadi-Gulyás , Éva Klement , Veronika Harmat , Maxim Petoukhov , Dmitri Svergun , Helena Zábranská , Michalea Rumlová , Iva Pichová , István Simon , Mónika Fuxreiter , Orsolya Barabás , Beáta G. Vértessy
Flexible segments modulate co-folding of dUTPase and nucleocapsid proteins
Nucleic Acids Res. , 35: 495-505. (2007) Kivonat -
Ibolya Leveles , Veronika Németh , Judit E. Szabó , Veronika Harmat , Kinga Nyíri , Ábris Ádám Bendes , Veronika Papp-Kádár , Imre Zagyva , Gergely Róna , Olivér Ozohanics , Károly Vékey , Judit Tóth , Beáta G. Vértessy
Structure and enzymatic mechanism of a moonlighting dUTPase
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. D69:2298-2308. | DOI: 10.1107/S0907444913021136 | PMID: 24311572 (2013) Kivonat -
Ibolya Leveles , Gergely Róna , Imre Zagyva , Ábris Ádám Bendes , Veronika Harmat , Beáta G. Vértessy
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of dUTPase from the φ11 helper phage of Staphylococcus aureus
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 67(Pt 11):1411-1413. | DOI: 10.1107/S1744309111034580 | PMID: 22102244 (2011) Kivonat -
Ildikó Pécsi , Ibolya Leveles , Veronika Harmat , Beáta G. Vértessy , Judit Tóth
Aromatic stacking between nucleobase and enzyme promotes phosphate ester hydrolysis in dUTPase
Nucleic Acids Res. 38(20):7179-7186. | DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq584 | PMID: 20601405 (2010) Kivonat -
Enikő Takács , Ibolya Leveles , Veronika Harmat , Anna Lopata , Judit Tóth , Beáta G. Vértessy
Direct contacts between conserved motifs of different subunits provide major contribution to active site organization in human and mycobacterial dUTPases
FEBS Lett. 584(14):3047-54. | DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.05.018 | PMID: 20493855 (2010) Kivonat